Google search console (formerly Google Webmaster Tools) is a free platform from Google which allows you to see how Google views your website. You can monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot the performance of your site. In addition, you can see your top-performing pages and for what keywords you rank on Google.
What’s the difference between Google Search Console and Google Analytics?
Google search console is focused on insights and tools that can help improve a websites presence on SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages). Google Analytics is user-focused, providing information on those that visit and use your website (what pages they visit/payments etc). If you don’t already have one, we highly recommend you get a Google Analytics account.
Top 6 functions of Google Search Console
While it can take a while to understand each function, it is worth learning what Google Search can do and how you can use these features to address any issues on your website and help improve your search engine rankings. Google Search Console can do many things that can improve your SEO and how Google views your website. Let’s take a little look at each of the features of Google search console:
- Ensures Google can crawl and index your site
The first and most important thing Google Search Console does is ensures that Google can find and crawl your site. Without this, you won’t appear in search results.
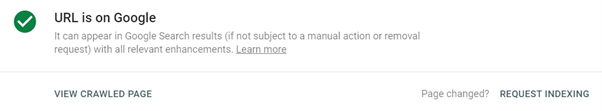
2. Allows you to fix indexing problems and request that Google re-indexes updated pages
New content can take anywhere between a few days up to a few weeks for Google to index, so don’t panic if it is not showing up straight away. Here is a breakdown of how to request Google re-indexes your site:
- Log onto your Google Search Console account
- Click the URL inspection tool option from the left-hand menu and then type your page URL into the search bar.
- Click on the REQUEST INDEXING button that appears towards the top of the page.
3. View traffic data to your site
This includes how often your site appears on Google Search and which search queries show your site, and how often searchers click through to your site from those queries.
4. Alerts you to spam, indexing issues and other issues on your site
If Google sees any issues on your site, it will alert you to issues pertaining to spam, indexing and so much more.
5. Show which sites link to your website
Backlinks are so important for SEO so it is worth knowing what sites are using linking to your site to ensure the quality of those links. We need to know that the sites that link to us are trustworthy and not spam as this could impact our own rankings and trust.
6. Troubleshooting
Google search console can troubleshoot any issues relating to mobile search, as well as other issues. Over 60% of internet searches these days are conducted using a mobile, so your site must be optimised for mobile.
Benefits of Google Search Console
While the above section gives an overview of what Google Search Console should do, this is going to look at the benefits of using Google Search Console for businesses.
The biggest benefit of Google Search Console is that it helps with your SEO efforts. One of the top ways to improve your SEO ranking can include tracking if the keywords you want to be ranking for are what searchers are using to find your website. Google Search Console also gives you metrics on your click-through rate, average position on SERPs and organic traffic. Additionally, you want Google to be able to crawl your website and index your content to ensure your site appears on searches. Google reports back any crawl errors for you to fix.
Another benefit is that Google Search Console analyses all aspects of your website and shows where errors are and where improvements can be made. This includes titles, URLs, and site links. By ensuring all these are meeting Google’s expectations, you have a better chance of ranking higher.
Google Search Console will show you if there are security risks to your website (such as potential hacking or malware). This is vital so you can attempt to solve the issue before it becomes a significant issue. Even better, you can set up email alerts if Google sees security or other issues on your website.
How to add your website to Google Search Console
- Open Google Search Console and enter your email address. This needs to be your business one, not your personal one (and a Gmail account. The easiest way to do this is to have a Gmail account for Google related apps. A simple businessname@gmail.com will be fine)
- You will then be asked I you want to use a URL Prefix property or a Domain property.
A URL prefix will report only on the metrics for that URL and nothing else (e.g. if you entered http://www.mywebsite.com, it would only search for those prefixes, not for https://mywebsite.com and so on.) Choosing this option will allow you to track a specific domain address without any subdomains.
Domain property will report on metrics from every combination of the subdomain and protocol (e.g., HTTP, HTTPS, m, FTP).
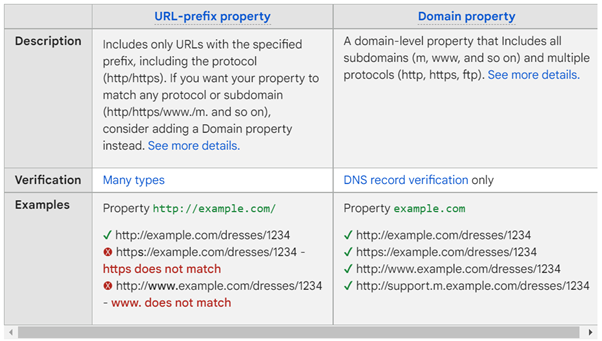
Source: Google Support - Once you have entered your details, you will be asked to verify your account. You can do this in several ways:
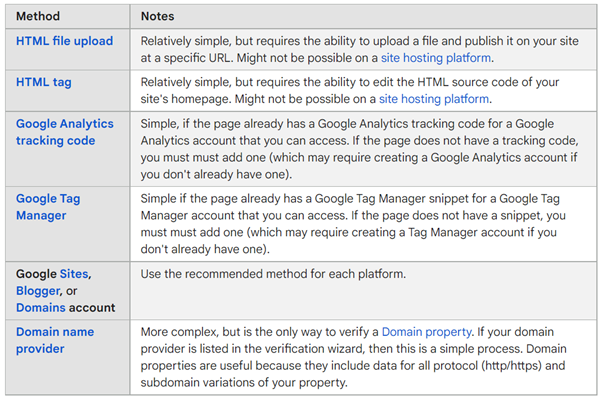
Source: Google Support (this link will also provide more detailed information about verification.)
How to use Google Search Console
Once you have verified you are the site owner, you can begin to use Google Search Console to optimise your website and fix any errors. Here we cover some of the basics of using Google Search Console and some of the key features which will be important to you.
You can get some remarkably interesting data from Google Search Console which can help you to improve your website.
Overview Report
While the overview gives a brief snapshot of your website’s performance, by delving into each tab in further detail you can get a more in depth analysis of your website.
URL inspection
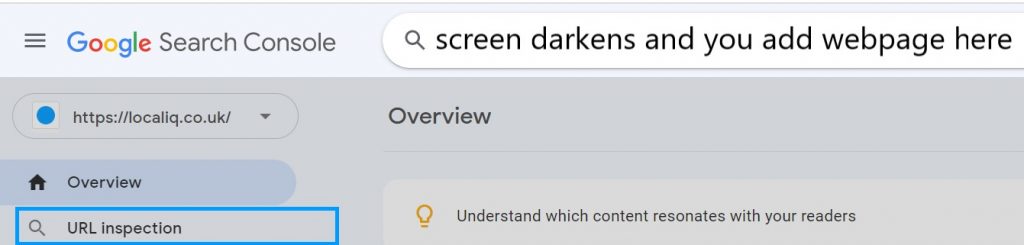
This is where you can input a URL from your website and check if the page has any errors in a comparable way to the overview but focusing only on one page.
Performance
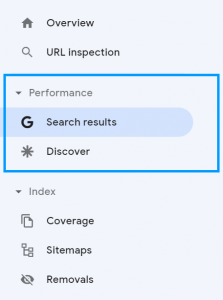
As you can see, from the image, the performance tab has 2 subcategories; search results and discover. Let’s break each sub category down and look at what data we are presented with.
Search Results
In search results, you are presented with two tables.
Table 1 is concerned with:
- Total number of clicks this is how many people clicked on your website.
- Impressions – An impression is when your website appears on a search even if a user did not actually see it. For example, if you were 9th on the page and the searcher clicked the 2nd result and did not see your page, it would still count as an impression.
- Click thru rate – what percentage of searches clicked through to your website. The equation is the number of clicks divided by the number of impressions.
- Position is where your site sits on average on searches. So, if you are the top result, your position will be number 1. Your average position is the average of your position for every keyword you rank for. The total sum of positions is divided by the total number of keywords. While on its own, this may not seem like the most important metric, it is a great tool for monitoring if your rankings change after you have made some on-page/site adjustments and optimisations.
Table 2 is concerned with:
- Queries – Here you can see all the keywords that you show up in search results across your website; essentially, how do searchers find your website?
- Pages – The pages with the most clicks. Here you can click on a particular page to analyse keywords for that particular page.
- Countries – Where in the world the searcher was
- Devices – What device was used to access your site (desktop/mobile/tablet)
- Search appearance – This is where you will find information on your featured snippets and videos
- Dates – Your clicks and impressions in date order (newest first).
Discover
Discover is a popular way for users to stay up-to-date on all their favourite topics, even when they’re not searching. In Google Search Console, the Discover report is shown to websites that have accumulated meaningful visibility in Discover, with the data shown back to March 2019.
Index
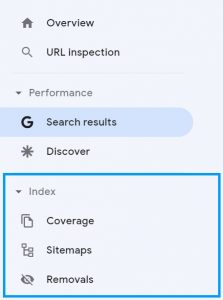
As we can see from the above image, Index is broken down into three subsections, coverage, sitemaps, and removals.
Coverage
This includes all how many pages Google has indexed and if there are any errors found. This also includes excluded pages. Each section is given a summary below.
- Error, this could be a server error or redirect error and has resulted in the page not being indexed.
- Valid with warning, these pages have been indexed but there may be an error on the page that needs fixing).
- Valid so these pages have been indexed
- Excluded are pages that have intentionally been excluded from indexing and won’t appear on Google searches
-
- Experience – Pages are broken down into web and mobile versions of your website here. This section is primarily concerned with page load speed, and page experience.
- Enhancements – ensures that your breadcrumbs and site links searchbox is working optimally.
The Details table includes what errors were found such as redirects, and server errors.
If you find that Google has not indexed any pages, you can submit a request. By clicking on URL inspection and entering the URL that you want to be indexed, Google will index that page. The indexing process can be completed in a few hours but could take up to a few days.
Sitemaps
Sitemaps are simply a map of your site highlighting navigation. A sitemap is important for Google to be able to properly index your site. If you currently do not have a sitemap, Google has produced an excellent guide to creating a sitemap.
Removals
Removals are used to remove a page from being found on Google. You can temporarily remove a page, remove outdated content, or submit a page for safe search filtering. In all these examples, you need to provide the URL for removal.
Experience
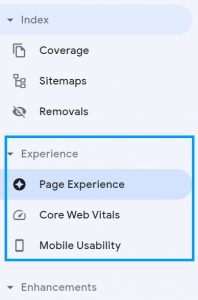
The experience tab gives an overview of what kind of experience a searcher has on your site. It is broken down into 3 subsections, Page Experience, Core Web Vitals and Mobile Usability.
Page Experience
This is the experience someone has on your site. You obviously want a user to have a positive experience on your website and ideally convert from a looker into a purchaser/subscriber etc. People will leave a site if the web pages are not to their satisfaction.
Core web vitals
Core web vitals also shows the experience a searcher has on your site. It is segmented by Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Display (FID) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). In essence, these are the load speeds, interactivity, and visual stability. These are vitally important as a poor website and load speed can mean a searcher leaving your site. Google has estimated that if a page does not load within three seconds, then the searcher will leave your site and find an alternative site.
Mobile Usability
This refers to how the website looks on a mobile device. If there are errors, such as images that don’t fit the screen, elements that are too close together and readability, then Google will mark those errors here for you to fix.
Enhancements
The enhancements tabs cover breadcrumbs and site links searchbox.
Breadcrumbs
A breadcrumb is a small text path on a website that shows where someone is. A breadcrumb string can effectively show a user how to navigate back easily.
Sitelinks searchbox
A search box allows users to be able to search effectively through your website. The reports here indicate any errors with your search functionality.
Security and Manual Actions
Manual Actions
You always want this to say no issues detected or you have a lot of work ahead of you! Manual actions could mean you are violating Google Guidelines. You need to find what is wrong, fix it and then submit a reconsideration request to Google.
Security Issues
These are when your site could have been hacked or you could have malware on your site.
Links
This is great for seeing which other sites link to your site (external links) and what pages on your site link to each other (internal links). If you click on any of the pages for internal or external reports, you will be able to see which websites have linked to a particular page. Your top linking text is the link text used by external pages that link back to your content. Your top linking sites are simply the sites that link to your pages and are outside of your website.
And there you have it. A comprehensive overview of Google search console and its features and benefits. We hope that you will find this useful in setting up and using search console. You can also read our Guide to Search Engine Optimisation to expand your breadth and knowledge of SEO.
How can LOCALiQ Help?
LOCALiQ are experts in digital marketing and have extensive knowledge of all of Google’s tools. If you would like some help with any of the tools mentioned in this article contact us today to see how we can help you. If you’re after the latest industry news, you can also sign up to our monthly newsletter.






