Over 5 billion search queries are made on Google daily, making it one of the most powerful platforms for paid advertising. In this guide, you will learn everything you need to know about advertising on Google, including how to optimise your campaigns to achieve the best performance and results.
- What are Google Ads?
- Benefits of using Google Ads
- Terms you need to know
- How Google Ads works
- Types of Google Ads campaigns
- How to set up a Google Ads campaign
- Step by step to setting up Google Ads
- 8 steps to successfully run a Paid Search Campaign
- Google Ads best practices
What are Google Ads?
Google Ads (formerly known as Google AdWords) is an online advertising platform developed by Google, where advertisers bid on keywords to display their advertisements, service offerings, product listings, or videos to internet users.
Google Ads allows you to create ads for all devices and specify a target audience for your business. Through the platform, you can advertise to the Google Display Network (GDN) which connects your offer with your target audience through multiple channels and placements, creating a positive experience for your prospects.

The platform works on a Pay-Per-Click (PPC) model, where the advertisers pay for every click or impression the ad generates. Once you have set up your audience and location targeting (more on this later), your ad will be displayed on the search engine results page (SERP) whenever your ideal customers are searching for products and services like yours on Google Search or Google Maps.
Benefits of using Google Ads
To be successful with PPC advertising, Google Ads should be part of your paid search strategy. Google Ads is the most popular search engine in the world and therefore an extremely effective way to drive high-quality traffic to your business. The platform connects your business with users searching for the products or services you offer, making it a win-win for advertisers and customers.
Google Ads helps you take advantage of online advertising through its detailed targeting options, costing controls, conversion tracking, and analytic tools to measure individual ad success and monitor overall campaign performance. This enables advertisers to achieve their business goals in a cost-effective way.
Below we have listed 10 benefits associated with Google Ads:
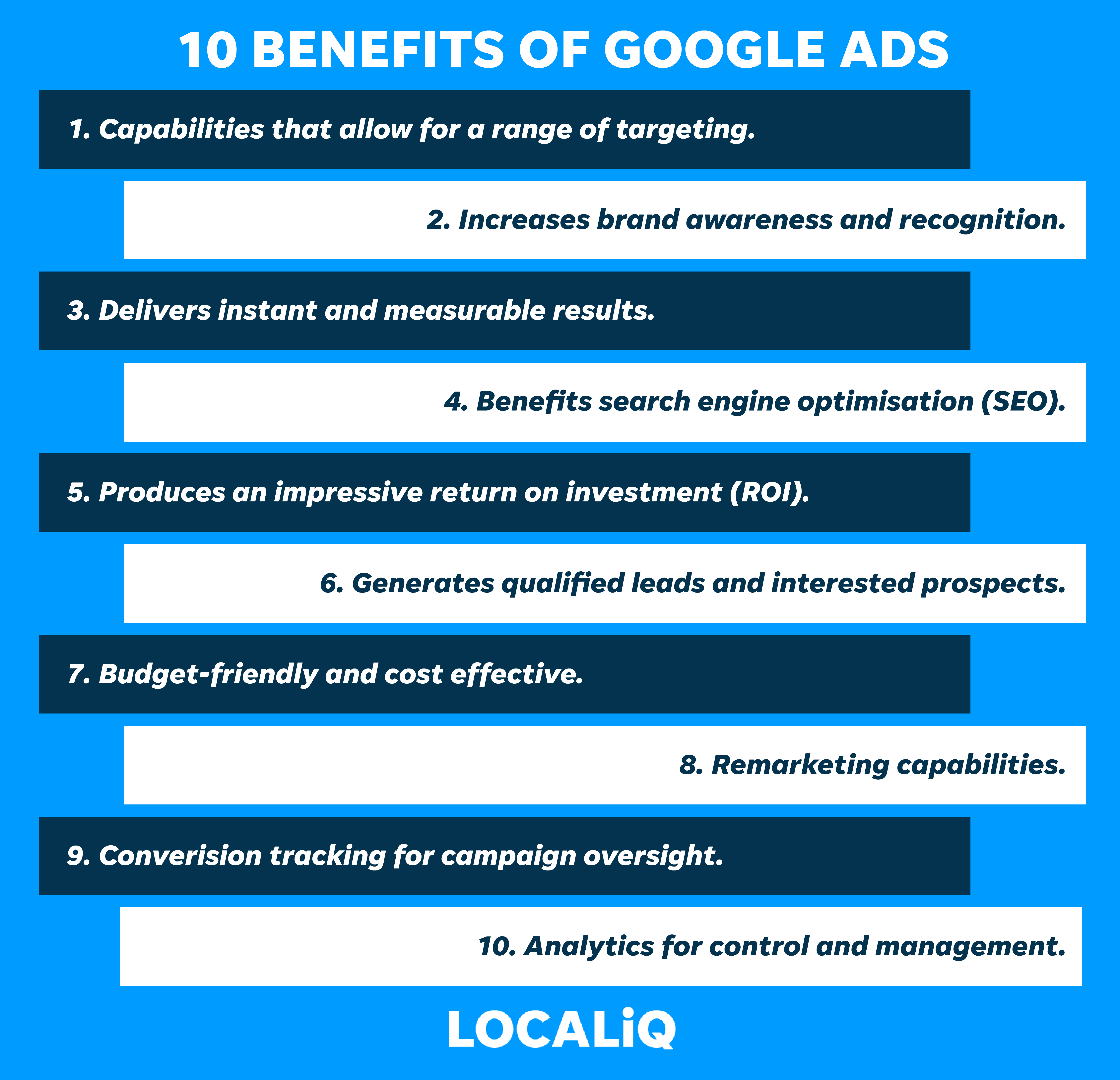
The greatest benefit of paid search ads is to guarantee your website listing appears at the top of the SERP. This helps to drive relevant traffic to your website, giving you an advantage over your competitors.
Additionally, paid ads are extremely time efficient; they can be set up in under an hour and your listing will immediately be displayed in the sponsored results.
Why should you be advertising on Google?
It is highly likely that your competitors have active adverts on Google to promote their business, and they could even be bidding on your branded terms. This means that even if you’re ranking organically for a keyword, your website listing will be pushed further down the SERP beneath your competitors.
The Google Ads platform is very accessible and easy to navigate for users, it will even provide relevant keywords and ad copy suggestions based on your website URL.
Terms you need to know
Here are some terms to keep in mind:
• Click Through Rate (CTR) is the percentage of users who land on your advertised page because they clicked on your ad (for example if your PPC ad made 100 impressions and 1 click, that’s a 1% CTR). A higher CTR generally means that your ad and keyword relevancy is better than others with a lower CTR. Google will look at your previous CTR and forecast future ones to determine how well your ad matches somebody’s search.
• Quality Score is a score measured on a scale from 1-10 which gives you a sense of how well your ad quality compares to other advertisers. Your Quality Score (QS) is how Google determines how your ad should rank. A higher Quality Score means that your ad and landing page are more relevant and useful to someone searching for your keyword, compared to other advertisers.
• Ad Rank is a value that’s used to determine where ads are shown on a page relative to other ads, and whether your ads will show at all. Ad Rank is essentially your Quality Score times the maximum bid you’ve selected, it is calculated using your bid amount, your auction-time ad quality (including expected click-through rate, ad relevance and landing page experience). Your Ad Rank is recalculated each time your ad is eligible to appear.
• Cost Per Click (CPC) bidding means that you pay for each click on your ads. The CPC is determined by the competitiveness of your keywords, maximum bids and your quality scores.
• Search Volume indicates how many times a certain keyword is searched for within a defined time frame. SEO marketers use this metric to determine how popular and competitive a keyword is. The higher the search volume the more popular the keyword and the higher the Cost Per Click (CPC).
• Keyword Difficulty is an SEO metric that estimates how hard it is to rank on the first page of Google for a given keyword. It is measured on a scale from 0 to 100, the higher the number the harder it is to rank for.
• Domain Authority (DA) measures the probability of an entire web domain to rank in the SERPs. DA works on a 0-100 scale with higher scores indicating stronger ranking potential. Sites with more backlinks and unique referring domains are more likely to have higher DA scores.
• Match types determine how closely a keyword matches the user’s search query, so an ad can be considered for auction. There are 3 ad match types: broad match, phrase match, and exact match. Google will automatically default to broad match because this is the most widely used ad match type.
• Ad Groups are a vital part of PPC marketing. They include all ads that share similar targets and are focused on a set of keywords in an ad campaign. When used correctly ad groups can drive traffic and leads to your site at a lower cost, resulting in more conversions.
How Google Ads works
Google Ads is essentially a marketplace where companies pay to have their website ranked at the top of a search results page. As previously mentioned, Google Ads works on a PPC model, making it a measurable and controllable marketing channel in comparison to more traditional forms of advertising.
PPC enables advertisers to bid on specific keywords relevant to their business. Whenever there is a vacancy for an ad on SERP, an auction takes place for the related keyword. At every auction, Google calculates an Ad Rank for every ad in the auction, which determines if the users see your ads in the first place.
There are currently six factors that define an ad rank:
- Your maximum bid on the keyword
- Ad quality and landing page experience
- Ad rank must be higher than the thresholds
- Competitiveness
- User search context (For example, device, location, time of day, and search intent)
- Expected impact of ad formats and extensions
The ad that wins the auction then immediately appears on the SERP and payment to Google is made when the ad is clicked, this is known as Cost-Per-Click (CPC). There are currently four available ad slots on top of the results and more ad slots are available at the bottom of SERP.
Google cares about its users so much that it’d rather show them a more relevant and better ad by someone who pays less because that keeps users coming back to Google. Therefore, the CPC can be lower than your maximum bid, especially if your ads and landing pages produce a good quality score.
Types of Google Ads campaigns
There is a variety of Google Ads campaigns you can choose from, the format you choose will vary depending on your business offerings and goals. There are 5 campaign types; Search, Display, Video, Apps, and Shopping.
1. Search
Search campaigns are the text ads that appear on search results and reach people while they’re searching on Google for the products and services that you offer. These are the most common type of ads that show up on the SERP above organic listings.
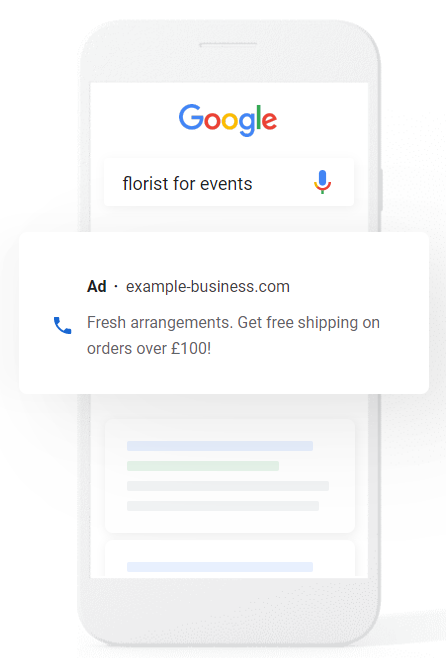
Text ads are simple ads, you decide the search term or keyword that triggers them and simply write your ad as you’d like it to appear. For a search campaign, you’ll select a goal, such as driving traffic to your website or increasing leads, and you’ll pay when your ad gets results e.g. people click your ad to visit your website or to make a call your business.
Here is an example of a search ad:
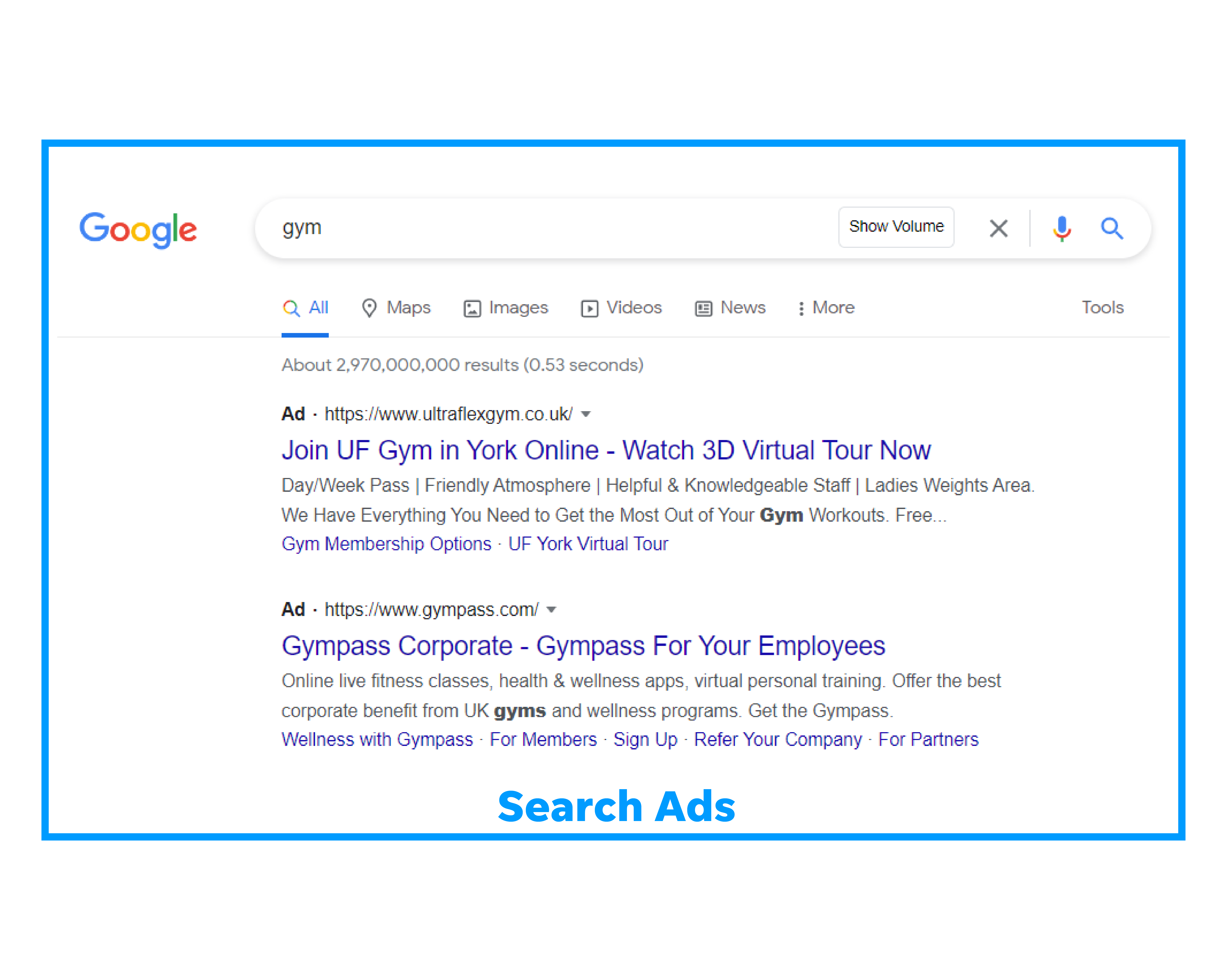
Search ads work best for targeting customers at the right time, and when used strategically, PPC campaigns are an excellent way to boost your visibility online, increase brand awareness, test new keywords, expand into new regions, and remarket to existing leads.
Learn how to create a search campaign on Google Ads.
2. Display
Display campaigns serve visually engaging ads on the Google Display Network. The Display Network helps you reach people as they browse millions of websites, apps and Google-owned properties (such as YouTube and Gmail).
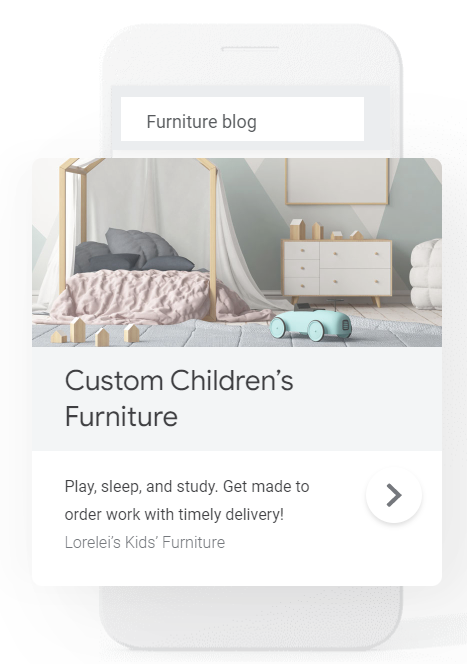
Display campaigns are a great way to expand your reach and stay top of mind with an audience beyond just Google Search. Display Ads, you can build brand awareness online faster.
Here are examples of a display ads:
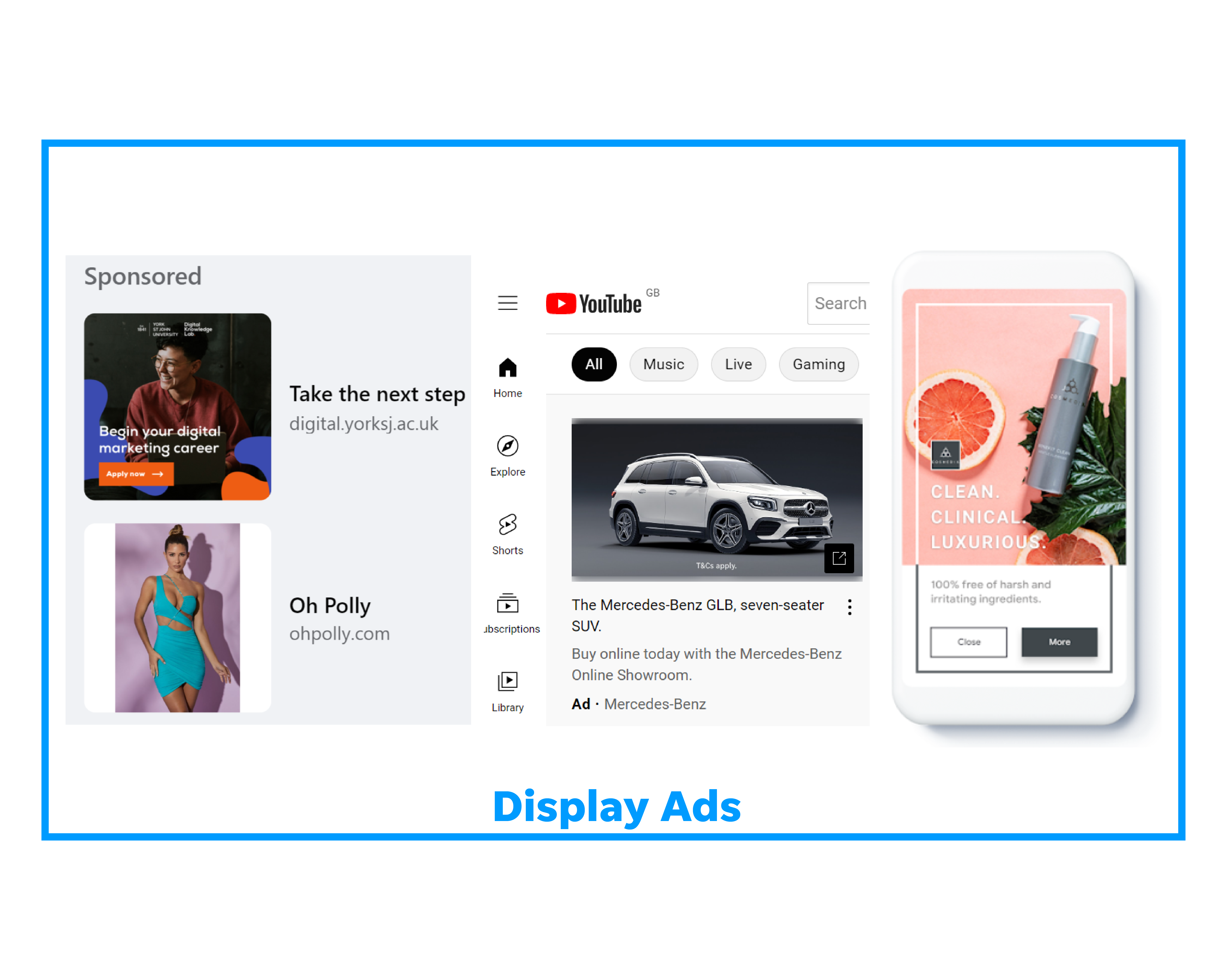
Learn how to create a display campaign on Google Ads.
3. Video
Google Ads offers a range of video ad formats so that you can create compelling videos with engage customers across YouTube and other video partner sites.
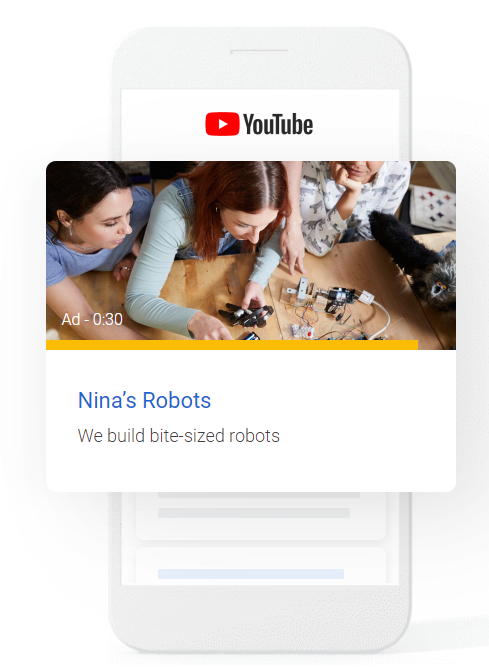
There are currently 6 available video ad formats to choose from:
- Skippable in-stream ads
- Non-skippable in-stream ads
- In-feed video ads
- Bumper ads
- Outstream ads
- Masthead ads
Here is an example of a video ad (with accompanying display ad):
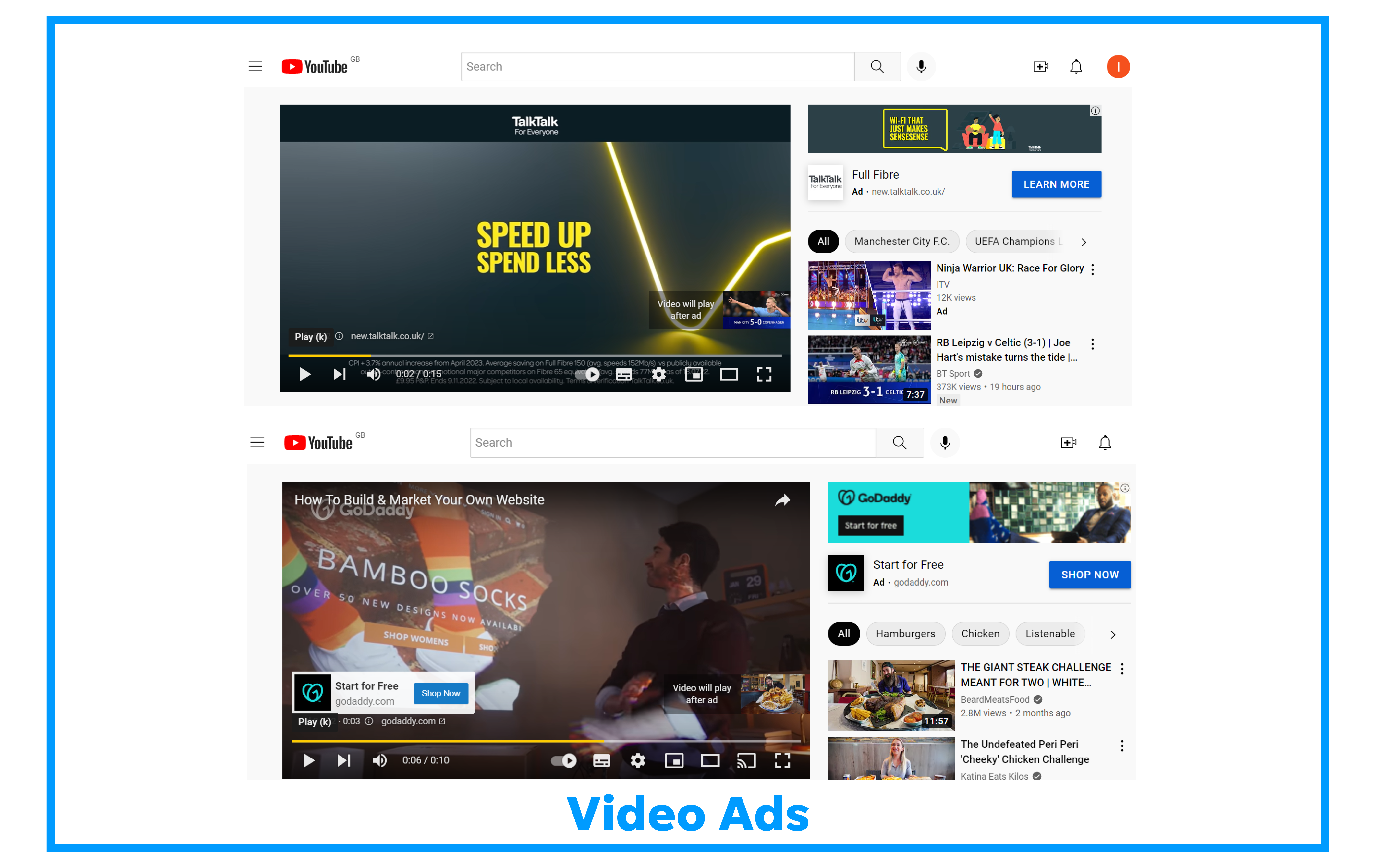
Learn how to create a video campaign on Google Ads.
4. App
App campaigns, enable you to promote your iOS or Android app on Google Search, YouTube, Google Play, and more.

The goal of these campaigns is to get new users to download and install your app. To do this you’ll want to optimise your campaign targeting, so it focuses on users most likely to complete app “events”, such as in-app conversions.
Here is an example of an app ad:
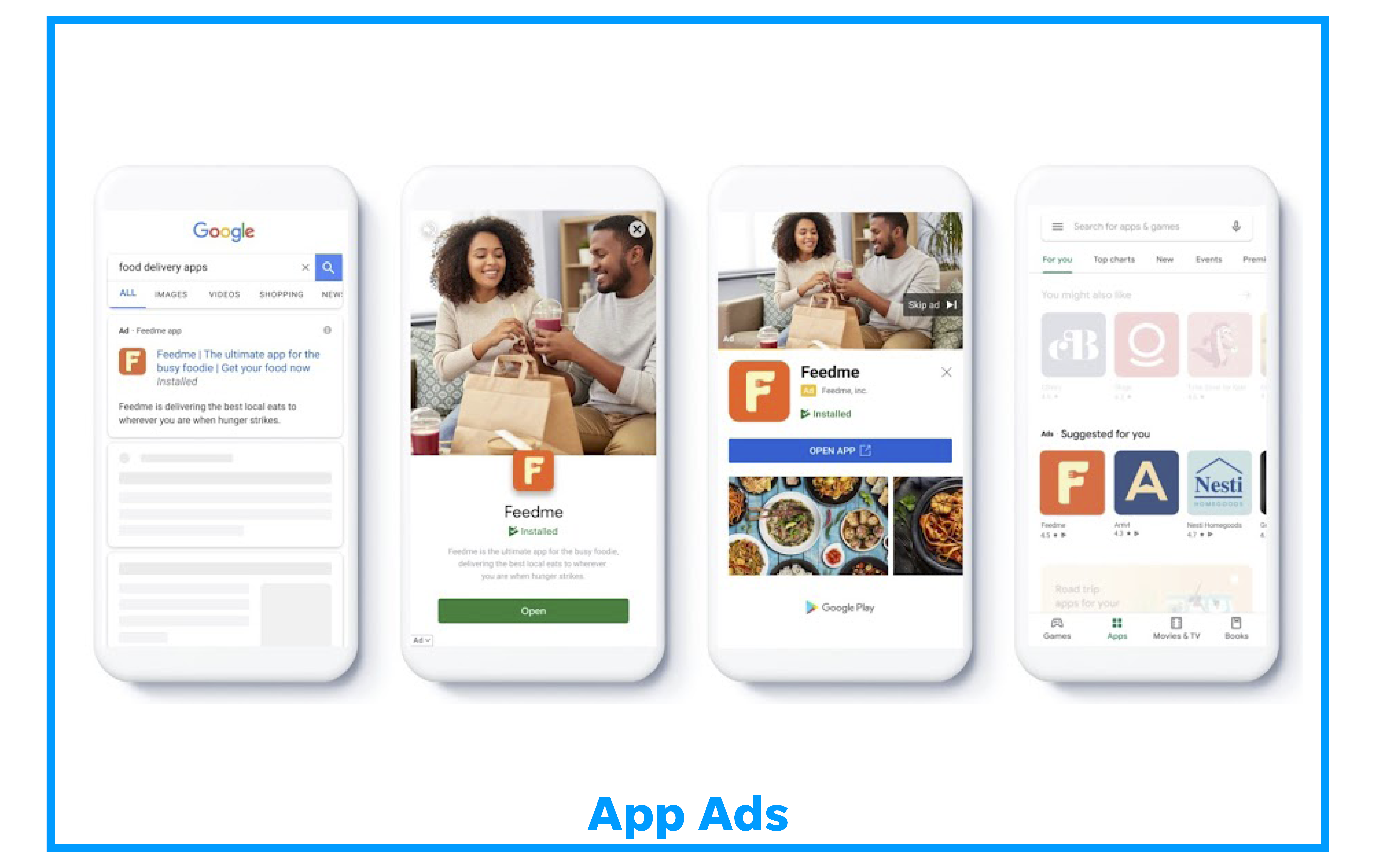
Learn how to create an app campaign on Google Ads.
5. Shopping
Shopping campaigns are product listings that are ideal if you’re a retailer looking to sell your product inventory. Shopping ads appear on search results and the Google Shopping tab. Shop owners can also use local inventory ads to promote products available at their physical locations.
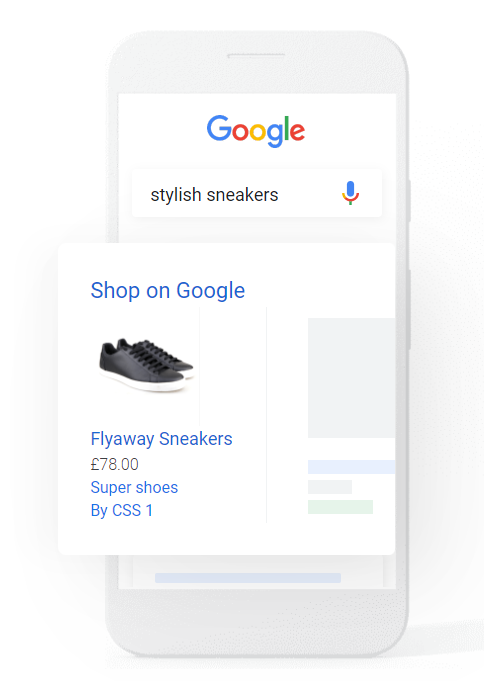
Here is an example of a shopping ad:
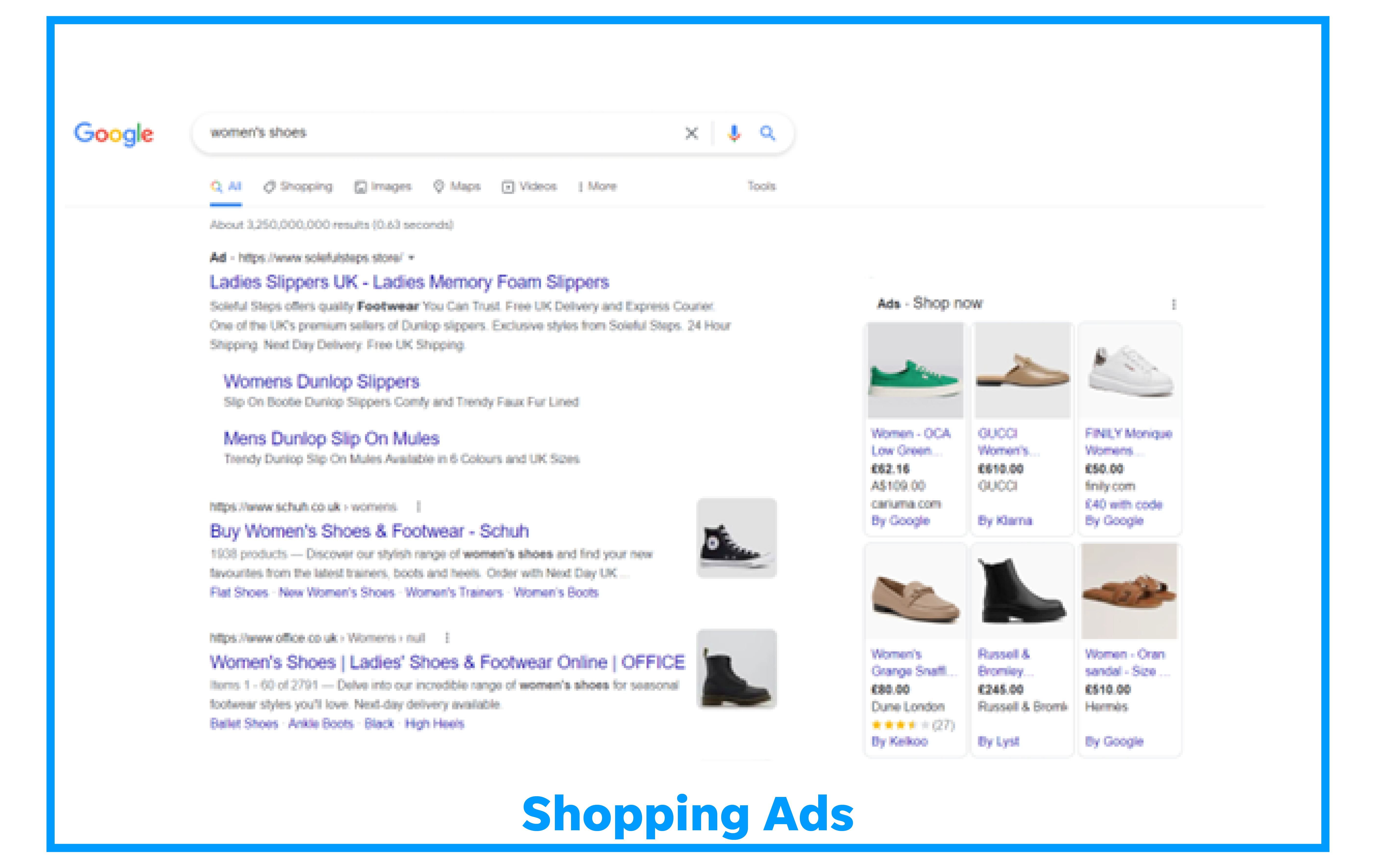
Learn how to create a shopping campaign on Google Ads.
How to set up a Google Ads campaign
Before we get started setting up a Google Ads campaign, there are a few things you need to decide. Google Ads offers different ways to target ads through its platform. Here is a breakdown of the available options to make marketing campaigns even more targeted:
- Keywords: Search terms, words or phrases that relate to your products or services, which are used to display your ads to customers who search for those terms.
- Ad location: Where your ads will be displayed on Google search results pages and websites that are part of the Google Search and Display Networks. You can also determine how often and what hours and days of the week you want your ads to appear.
- Audience Targeting: Select the age, geographic location, and language of your customers.
- Devices: Ads can appear on all types of devices, and you can specify which devices your ads appear on and when.
Keywords
Anything searched on a search engine, whether a single word or a phrase, is considered a keyword. Preferably you want to target keywords which have a high search volume (the number of times a particular keyword is entered into a search engine per month) and a low keyword difficulty (a metric used to determine how difficult it is to rank for a keyword).
Types of Keywords
There are three types of keywords:
- Head terms (also known as fat head) = are single-word keywords with high search volume, however, they’re much more competitive, meaning they are difficult to rank for (e.g. coffee).
- Body keywords (also known as Chunky or Middle) = are 2-3 word phrases with decent search volume. These are slightly more specific than head terms and therefore are slightly less competitive (e.g. coffee machine).
- Long-tailed keywords = are usually several words long. These phrases typically have a low search volume, however they are much less competitive because they are narrowed down to a niche topic (e.g. which coffee machine is best for home).
You will need to know keyword terms such as ‘Search Volume’, ‘Authority’, ‘Relevance’, ‘Trends and Projections’ to effectively conduct keyword research, if you’re not familiar with these terms then check out our blog.
Location targeting
Location targeting, also referred to as ‘geotargeting’, is a way to select specific locations where you want your ads to be shown. This type of advertising uses location data including users’ settings, devices, demographics, and behaviours to reach consumers with tailored messaging appropriate to their locality.
Geotargeted marketing is hugely advantageous for businesses that only sell products or provide services in specific locations. For example, if your restaurant is situated in Manchester, you’ll want to set your search campaigns to only show to searchers in and around Manchester. It is more realistic that consumers in this area will visit your restaurant due to its proximity.
Without location targeting, you’ll risk wasting your ad spend on showing ads to consumers outside of relevant areas, resulting in unnecessary impressions and clicks chipping away at your marketing budget without any kind of return.

Types of Location targeting on Google Ads
There are two main types of geotargeting, “physical location” and “location of interest”.
- “Physical location” will target people that are currently in the targeted locations.
- “Location of interest” will target people with search interest in that location (such as a modified search query, someone who was recently in the area, or someone planning to visit to the area).
Google gives you the option of whether you’d like your ad to appear for someone’s physical location, locations of interest, or both. Depending on the geotargeting type you choose, Google Ads will use a range of factors to determine the user’s location.
The Google Ads system determines physical location based on:
- IP address
- Device location
- GPS
- Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth
- Google’s cell ID (cell tower) location database (used in the absence of Wi-Fi or GPS)

Everything you need to know about targeting geographic locations in Google Ads.
Google Ads allows you to target users based on specific countries, regions, or even by a radius around a particular location. If you don’t specify a target location, Google Ads will assign all countries and regions to your campaign by default resulting in wasted ad spend.
Google Ads also gives the option to exclude people based on certain locations. For instance, if you only ship within the United Kingdom, you’ll want to exclude anyone outside of the United Kingdom.
Audience targeting
If you’re new to paid advertising on Google, you might have to experiment with different targeting options until you reach an audience that is right for your business. Google ads targeting lets you refine the group of people you want Facebook to display your audience to and build your own customised audience based on demographics, interests, and behaviours.
Remember that any target audience you create, Google Ads will automatically try to find relevant people to achieve your set campaign objective. Therefore, you don’t have to worry about refining the audience too much.
Step by step to setting up Google Ads.
Step 1: Go to your Google Ads dashboard.
Step 2: To create a new campaign either click “+ New Campaign” from the Overview or go to “Campaigns” from here you can either create a new campaign or edit an existing one.
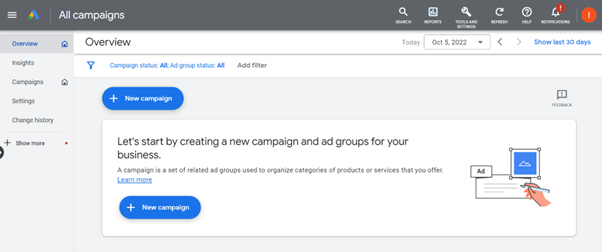
Step 3: The first thing Google asks you to do is select your campaign objective. Each one has a brief explanation to help you choose the best business goal for the campaign (for this example we have chosen website traffic as the objective).
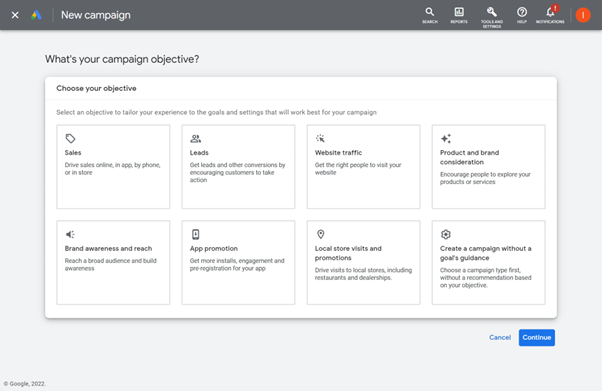
Step 4: Next Google asks you to choose a campaign type from the options we discussed earlier (for this example we have selected ‘Search’).
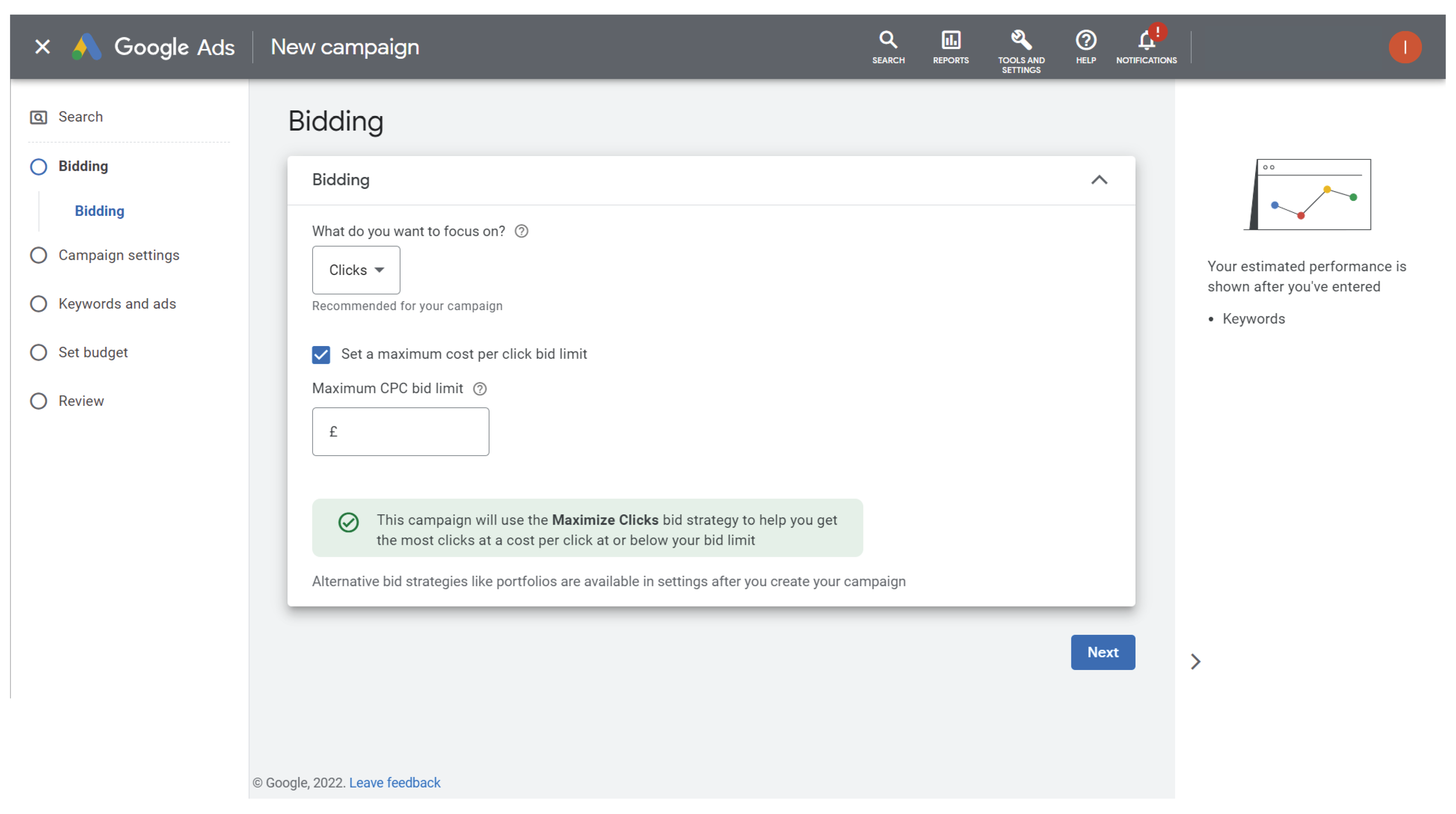
Step 5: Once you have selected your campaign goal and campaign type you will be ready to set up your bidding settings. Here you can choose from the dropdown menu whether you want the campaign to focus on the number or clicks or number of impressions your ad generates. Google also gives you the option to set a maximum cost per click bid limit to ensure you don’t exceed your budget.
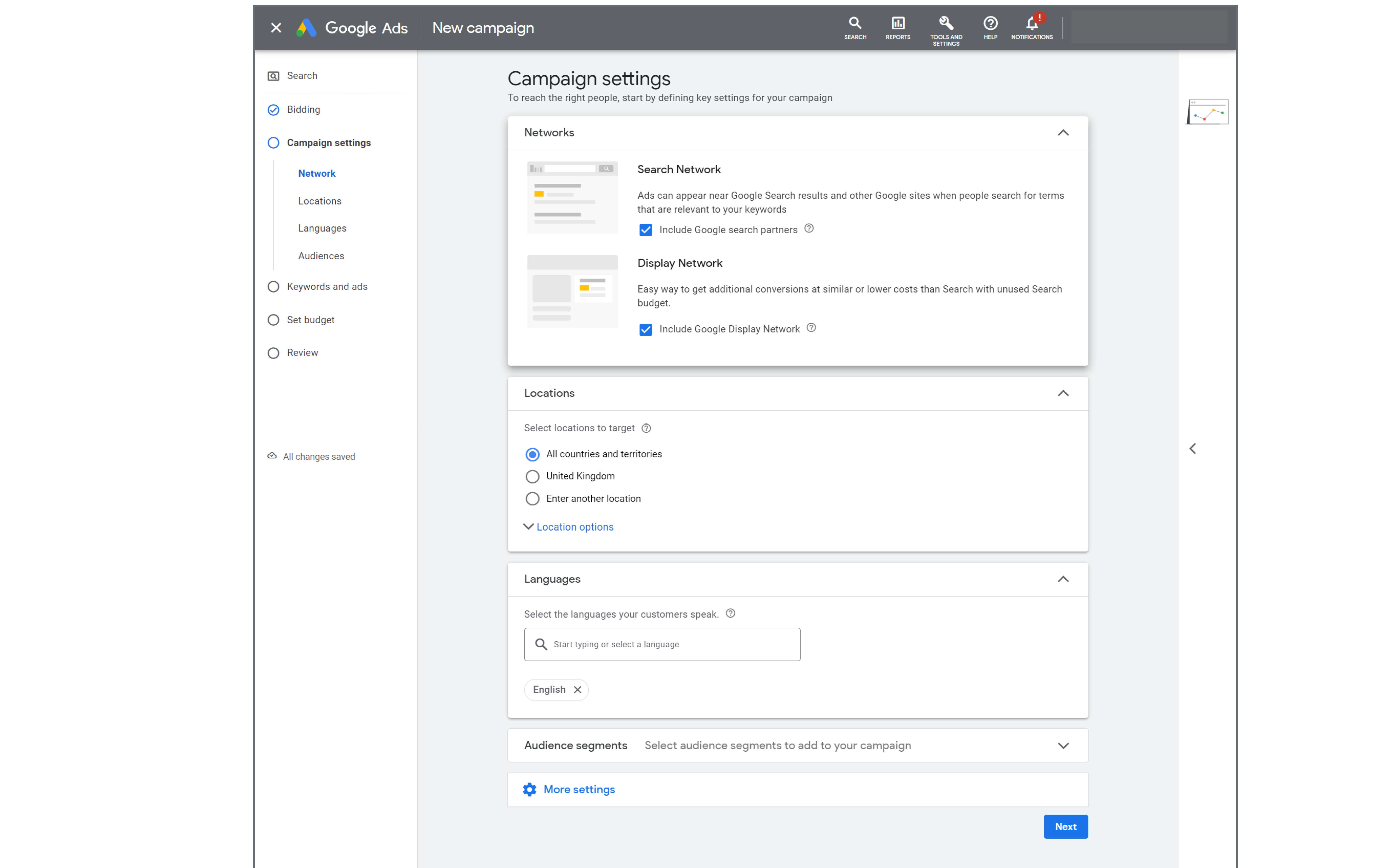
Step 6: Now you are ready to tailor the ad campaign to make sure you reach the right audience. This section includes Networks, Locations, Languages, and Audience settings. The Google Network is divided into groups to give you more control over where you’d like your ad to appear.
- The Search Network = Google search results pages, other Google sites like Maps and Shopping, and search sites that partner with Google to show ads.
- The Display Network = Google sites like YouTube, Blogger, and Gmail, plus thousands of partnering websites across the Internet. To optimise your campaign to its full potential we recommend having both Networks enabled.
Step 7: Google Ads permits you to run different ads in different locations so that they can be optimised for specific audiences in each place. Here you want to pick a specific country, city, or postal code and type it into the field. Google Ads system will then provide a list of locations which match the area you have entered. From there, you have the option to select from ‘target’ ‘exclude’ or ‘nearby’ to indicate whether you want to target that specific region, exclude it from displaying your ads, or target the nearby surrounding areas of that place.
There is an additional ‘location options’ dropdown that can be further used to specify who you want your ads to be targeted at. The “target” setting allows you to select who will see your ad based upon locations you’ve added to target while the “exclude” setting allows you to choose which people will be excluded.
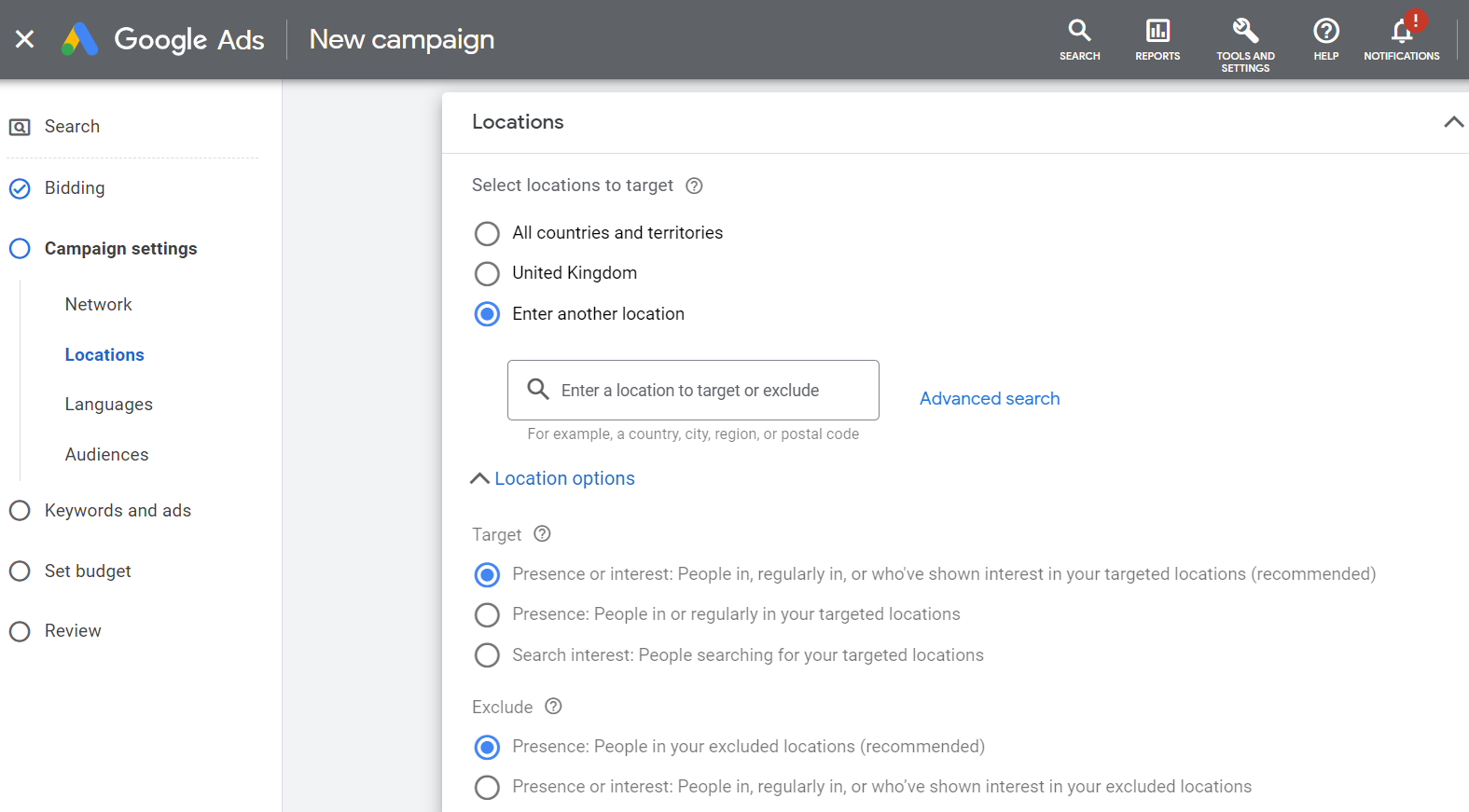
If you want your ads to be more targeted around a specific radius you’ll want to use radius targeting. To do this select ‘Enter another location’, click ‘Advanced search’ and a pop out box with an interactive map of the world will appear. Enter the name of the place or its coordinates, then select the number of miles radius you want to implement, check the map to ensure you are targeting the correct area, and click ‘Save’.
If you are editing an existing campaign, simply click the name of the campaign you wish to edit, click the blue pencil icon, then select Radius, and enter the name of the place and its coordinates following the rest of the steps previously mentioned.
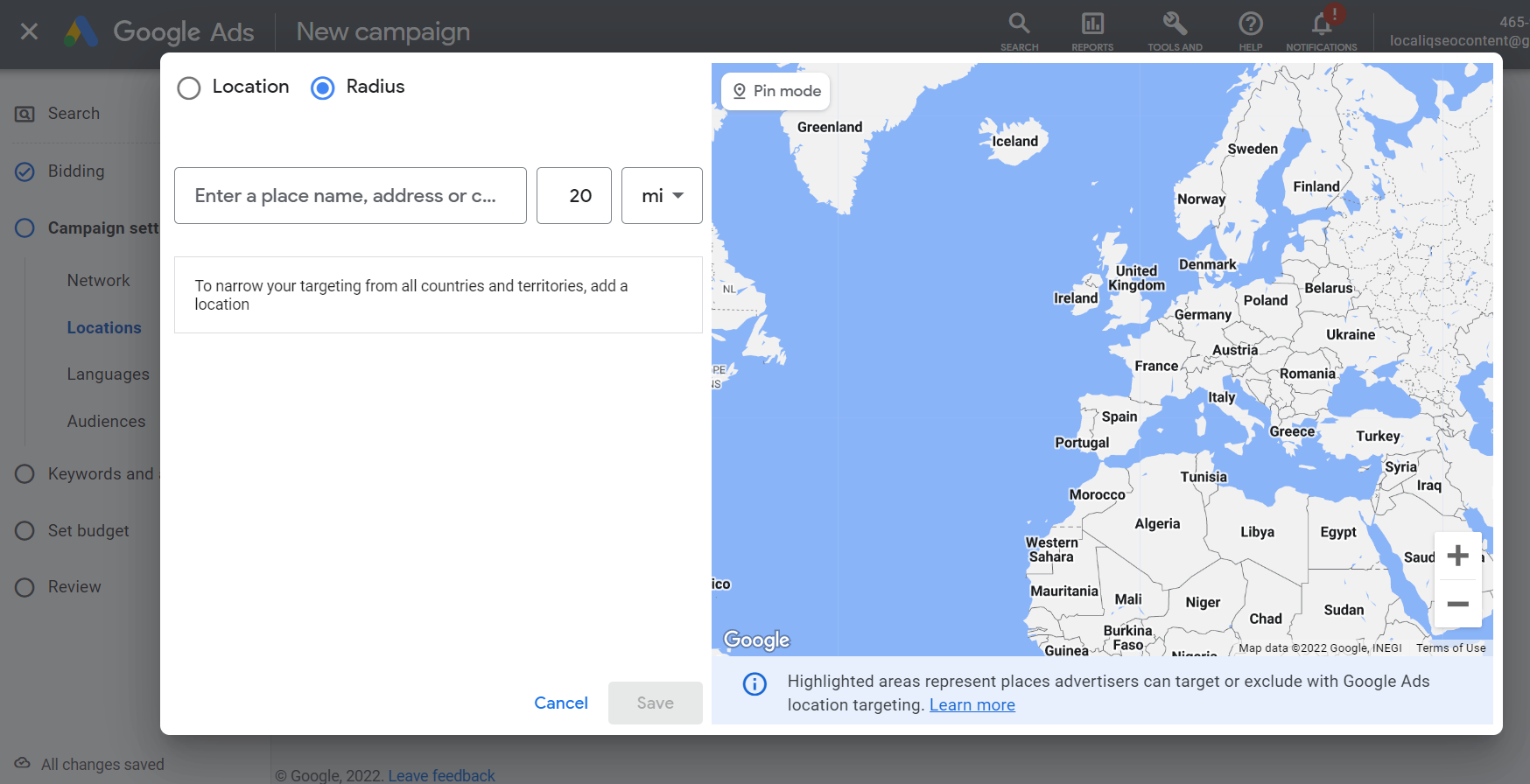
Remember: selecting a small radius could mean that your ads might only show intermittently or not at all. That’s because small targets might not meet Google’s targeting criteria.
Step 8: The languages sections is rather self-explanatory; simply type the language(s) your customers speak so that ad will be legible by your target audience.

Step 9: Audiences are the groups of people with specific demographics, interests, and intent, as estimated by Google. You can either manually ‘Search’ for specific interests, job titles, demographics or you can ‘Browse’ Googles audience segments. There is a wide range of options to choose from, so if you are unfamiliar with this section play around and see what best represents your customers (you’ll want to have your buyer persona at hand to help define your target audience).
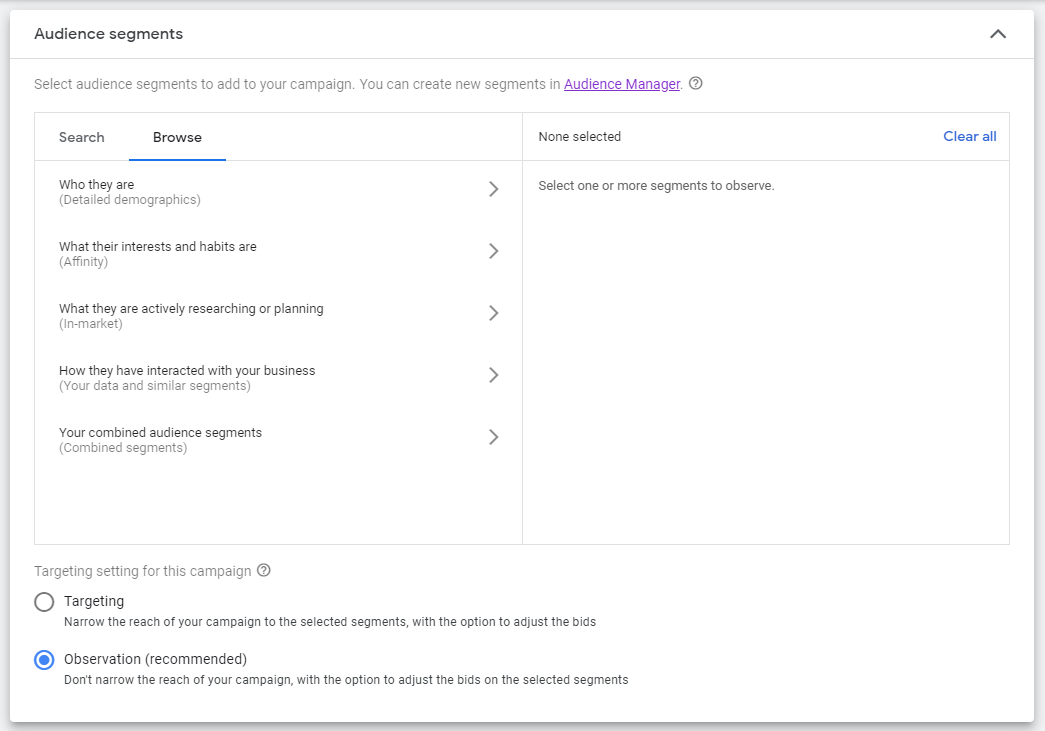
Remember: Adding too many targeting options or restrictions may limit your campaign’s reach.
The targeting settings below the audience segment section enables you manage whether to let the selected segment to narrow the reach of your campaign. Both settings allow you to adjust the bids or set custom bids.
- Targeting: Narrows the reach of your ads to specific criteria in this method.
- Observations: Reports how your ads perform on selected criteria.
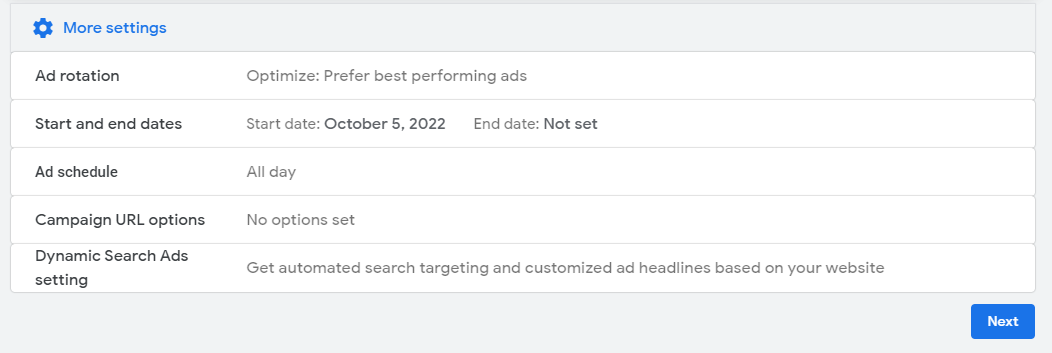
Step 10: There is a dropdown box if you click ‘More Settings’. Here Google gives you the option to amend any pre-set settings such as start and end dates, campaign URL etc. To edit any of these additional settings hoover over the setting and click the pencil on the right to edit.
Step 11: Once you have completed your audience settings, you’re ready to enter your keywords. You can either enter your keywords manually in the big box (remember to focus your keywords on the product or service you are trying to promote).
Alternatively, Google Ads gives you the option to enter a URL or the name of a product or service, so they can scan the page and make keyword suggestions.
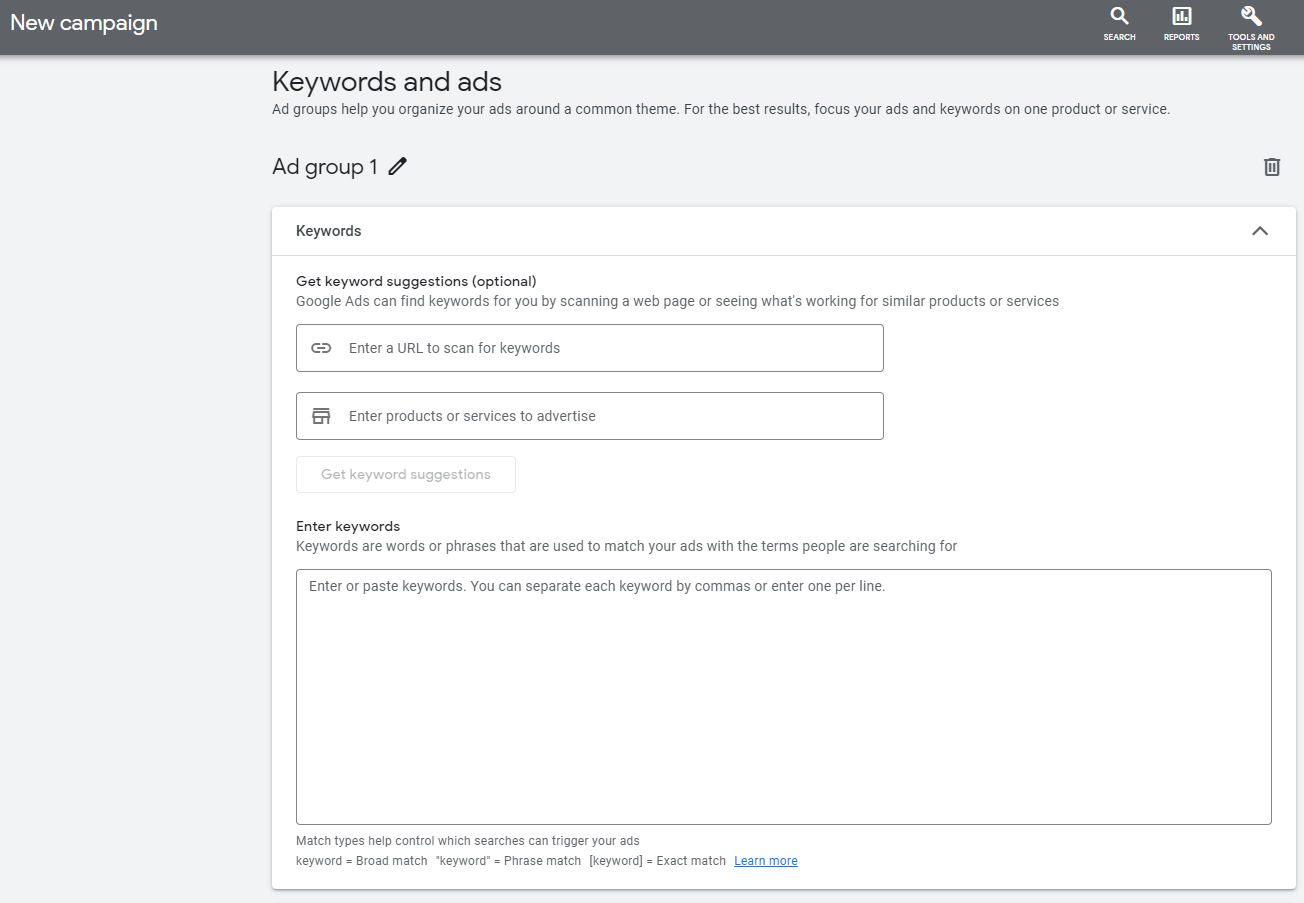
Need help choosing your keywords? Check out this blog for the best free keyword research tools.
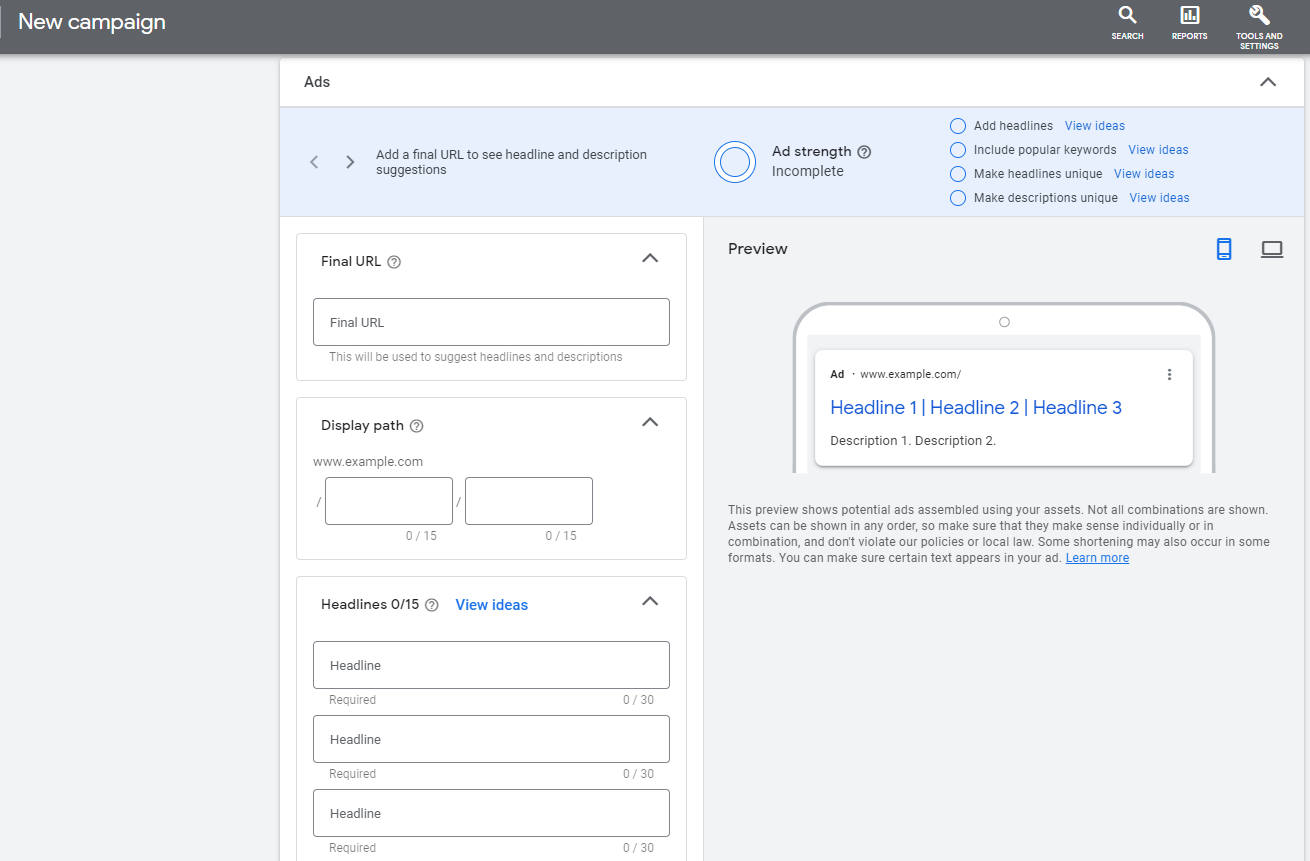
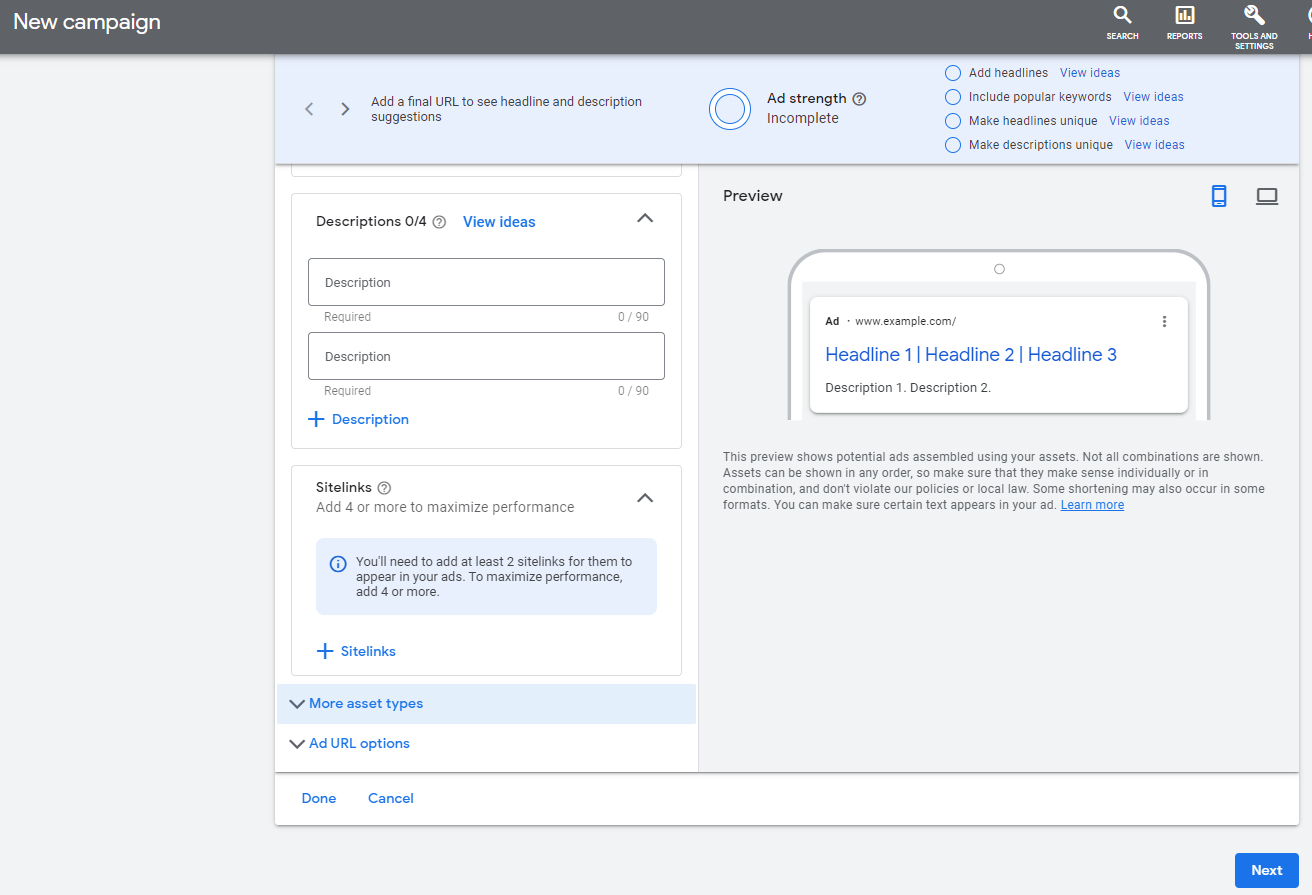
Step 12: It’s time to build your ad. Depending on the campaign type you have chosen this stage may slightly vary. One of the great things about Google Ads is they will actually make suggestions for ad headlines and descriptions based on your business website.
You can use up to 30 characters in the ad headline and up to 90 characters in the ad description.
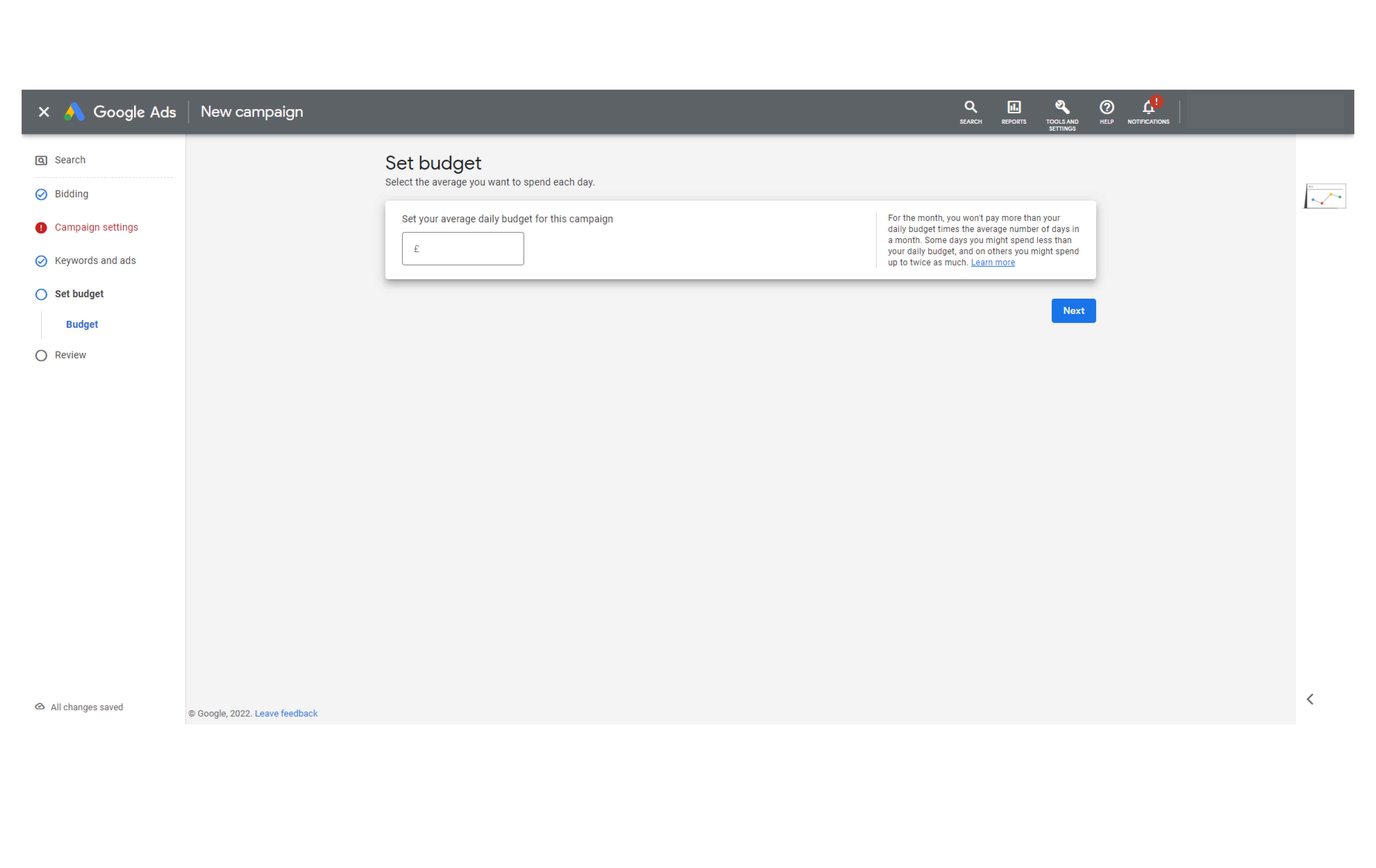
Step 13: The last step of the campaign set up is to set your budget. Simply enter the average amount you want to spend each day.
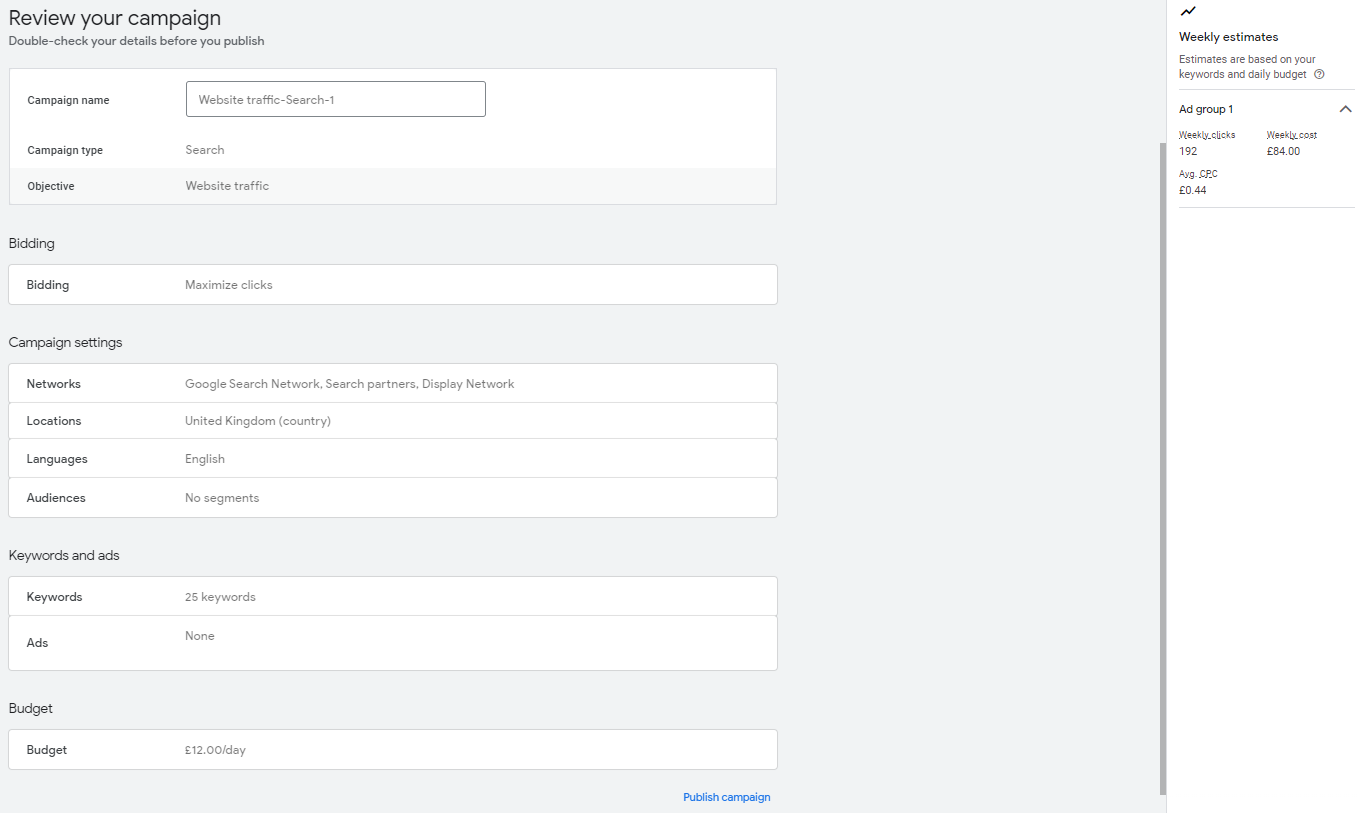
Step 14: The final thing to do before you can set you ad live is to review your campaign. Here you’ll want to double check everything and take a look at the weekly estimates predictions on the right side which give you an idea of how many clicks your ad will generate and the average cost. Once you are happy with your settings click ‘Publish’ and your ad will be set live.
8 steps to successfully run a Paid Search Campaign
- Set a goal for your PPC campaign
- Analyse keywords
- Choose your match type
- Create your ads
- Focus on the language of your PPC copy
- Use Ad Groups
- Optimise paid ads for mobile
- Be strategic with budget
Find out how to successfully run a paid search campaign.
Google Ads best practices
- Choose a campaign goal and keep it top of mind when creating your ad.
- Use a PPC planning template (with Google and HubSpot’s PPC Planning Template, you can view how your ads will appear online, see your character counts, and manage your campaigns all in one place).
- Choose keywords with a high search volume and low keyword difficulty.
- Align your keyword strategy with your bidding.
- Improve your Quality Score (The higher your QS, the better your rank and placements on the Search Engine Results Page).
- Optimise your ad landing page (Review landing page best practices and implement them to increase your conversion rate).
We hope you’ve found this guide helpful. At LOCALiQ we love paid search marketing and run many campaigns for a variety of clients across a wide range of industries. If you’d like additional help with setting up Google Ads, contact us today for a free consultation.
Here are some further resources you might be interested in:
Google Ads Destination Requirements Policy Update.
How to Set up Location Targeting in Google Ads.
Tips for Conducting Effective Keyword Research.
How to Successfully Run a Paid Search Campaign for Businesses.
What are Featured Snippets? And How To Get Them.






